What is Dom?
- Catalogs the web page into individual objects that we can select and manupulate.
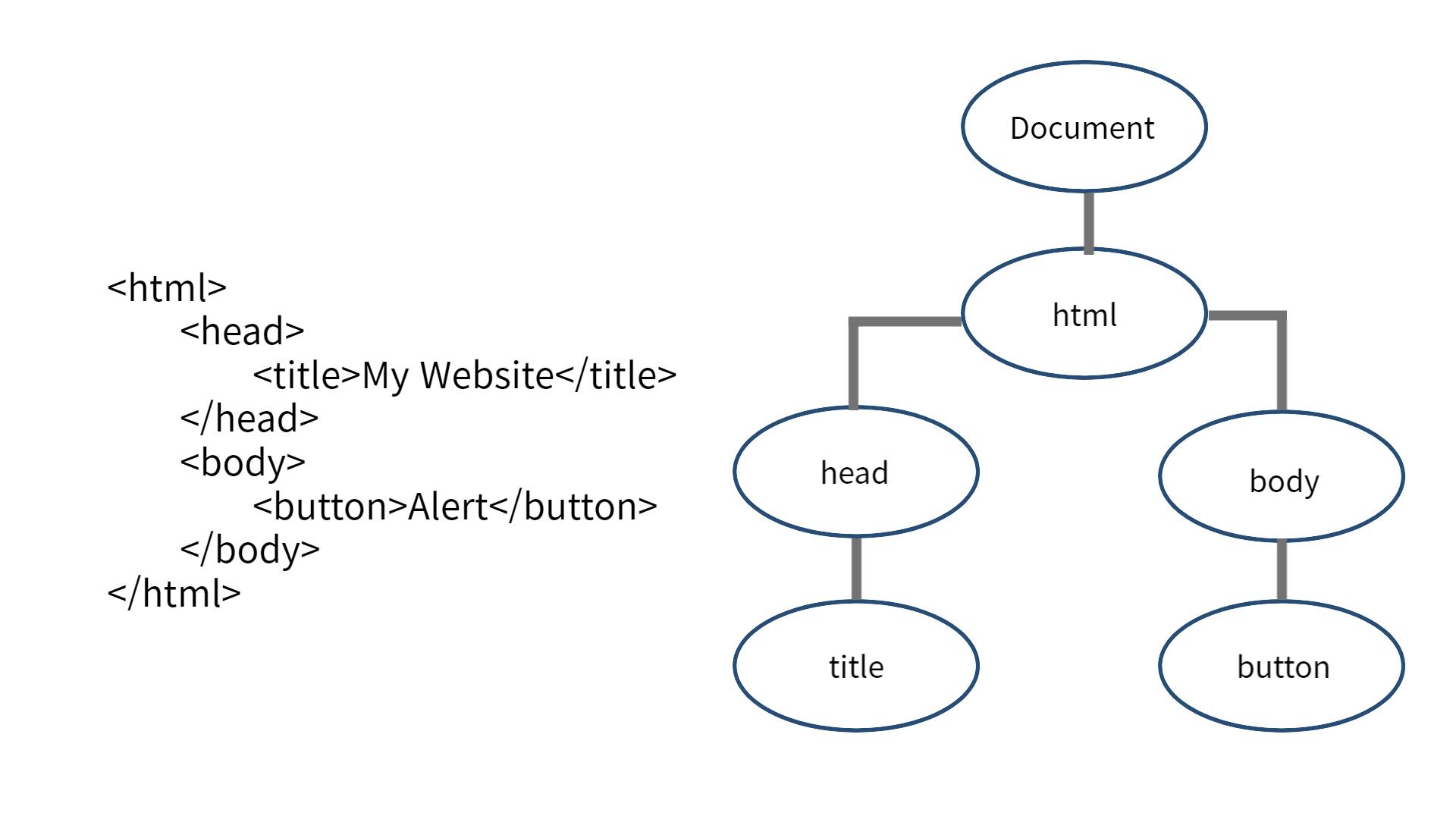
How to select objects using Dom?
var heading = document.firstElementChild; // first child of whole document.
var footer = document.lastElementChild; // last child of whole document.
var input = document.querySelector("input"); // You can select an element by css selector.
var p = document.querySelectorAll("p"); // Select all paragraph tags
var highlight = document.getElementbyId("highlight"); //Select an element by Id
var bold = document.getElementsbyClassName("bold"); //Select elements by class name
input.click(); // simulates mouse click.
heading.innerHtml = "Good Bye"' // -> <h1>Good Bye</h1>
heading.style.color = "red"; // css: color : red;
Getter
If our object was called car, then we can say car.color to get the value of the property
var color = car.color; // return the variable color from object "car".
Setter
car.color = "red"; // Set the color variable of object "car".
Method
car.drive(); // Car will drive
Function VS Method
Method is something that an object can do. It has to be associated with an object.
How do you change the style in JS?
- JS variables and functions and methods are camel case. So When you change your style by JS, the properties are also in camel case.
- Style values are all in string type.
Add a class to an element
// <button class="btn"></button> -> <button class="btn invisible"></button>
document.querySelector("button").classList.add("invisible");
// <button class="btn invisible"></button> -> <button class="btn"></button>
document.querySelector("button").classList.remove("invisible");
// If the class invisible is already applied then remove it.
// If the class invisible is not applied, then apply it.
document.querySelector("button").classList.toggle("invisible");
TextContent
document.getElementById("title").textContent = "Good Bye"
TextContent vs InnerHTML
InnerHtml gives you elements in element you selected as well as just Text In elements but textContent only gives you a text in an element you selected.
Manupulating HTML element attributes
// You can see all the attributes that a tag has.
document.querySelector("a").attribute;
// getter
document.querySelector("a").getAttribute("href");
// setter
document.querySelector("a").setAttribute("href","bing.com");
Event Listener
// We are waiting for the click to happen before we call the functionName function.
// So There is no parentheses here even though It is a function.
document.querySelector("button").addEventListener("click",functionName);
// anaymous function
document.querySelector("button").addEventListener("click",function(){console.log("click!")});
Higher Order Functions
Functions that can take other functions as inputs.
function add(num1,num2){
return num1 + num2;
}
function subtract(num1,num2){
return num1 - num2;
}
function multiply(num1, num2){
return num1 * num2;
}
function divide(num1,num2){
return num1 / num2;
}
function calculator(num1, num2, operator){
return operator(num1,num2);
}
console.log(calculator(7,5,subtract));
